Análise de licenciamento da marca ajuda os proprietários de marcas a notar áreas de melhoria, orientar o investimento e maximizar o crescimento do valor. Para PepsiCo para Shell. O licenciamento da marca requer a auditoria formal da propriedade da marca (e da IP) e usa sua avaliação e preços. Também ajuda a colocar marcas e licenciamento no centro da tomada de decisão. Consulte o nosso
Intangible assets work together to multiply business value by increasing revenue, finding cost efficiencies and reducing risk, and mapping those interactions helps to maximise these effects.Setting up a central BrandCo is the best way to measure, manage and invest in brands and most of the best companies in the world - take it from Apple to PepsiCo to Shell.
The process of identifying intellectual property, understanding it's value and contribution to the business and pricing it according to performance helps business directors to notice areas of improvement, guides investment, and maximise value growth. Brand Licensing necessitates the formal auditing of brand (and IP) ownership and uses its valuation and pricing. It also helps to put brands and licensing at the heart of decision-making.
In order to get it right from the offset, this article is intended to show how to understand the way in which brands and intellectual property create value, as well to illustrate the characteristics of successful businesses.
Make licensing decisions using hard data. See our Serviços de consultoria para obter mais detalhes, ou Entre em contato conosco diretamente. Adoramos conversar.
- Economia de ativos intangíveis
- As marcas funcionam com outros intangíveis para criar valor e crescimento ...
- como você garante que o licenciamento interno ou externo do ecossistema de licenciamento da marca = o maximize os benefícios e minimize 130 ... Ritz-Carlton
- Case Study: Ritz-Carlton
- Case Study: McDonald’s
- Case Study: Multinational Telco Operator
- Conclusion
Economics of Intangible Assets
To understand the appropriate way to manage, invest in and exploit the value of brands and other intellectual property, it is useful first to grasp the way brands are build and how they build Valor nas empresas. Para ser valioso, a tecnologia, as marcas comerciais e outras propriedades intelectuais precisam trabalhar juntas para gerar fluxos de caixa - normalmente criando eficiência de custos, aumentando a demanda/preço ou reduzindo o risco. Por exemplo:
It is a well-established fact that the value of businesses is determined by the free cash flows they are able to generate for holders of their shares and debt. In order to be valuable, technology, trademarks and other intellectual property have to work together in order to generate cash flows – typically by creating cost efficiency, increasing demand/price or reducing risk.
First, however, it is important to understand how the economic characteristics of IP are different from tangible assets. For example:
- O valor do IP geralmente não é reduzido através do uso e pode ser usado simultaneamente por várias partes
- O custo da construção de IP geralmente não está intimamente relacionado ao valor resultante. Existe um alto risco de investimento desperdiçado (principalmente quando o conceito não é testado), mas há alto potencial de vantagem se a propriedade for comercializada com sucesso. é geralmente uma coleção de direitos individuais que derivam valor como resultado de serem licenciados juntos como um (por exemplo, um domínio, marca registrada, slogan, logotipo etc. compõem uma "marca"). A interação entre diferentes ativos depende: a qualidade do IP e seu gerenciamento; a indústria; o país; e o estágio da vida dos negócios, entre outros fatores. A inovação é importante para começar, mas isso impulsiona a reputação, o que agrega valor e pode sustentar uma empresa por períodos de menor inovação. O conhecimento dessas interações ajuda a entender quais taxas devem ser cobradas, mas também como concentrar o investimento.
- IP derives its value by being used with other assets (tangible and intangible).
- IP is commonly licensed on its own but generally sold as part of a business, so royalty payments are often available but individual Values are not.
- An individual “asset” is usually a collection of individual rights that derive value as a result of being licensable together as one (e.g. a domain, trademark, slogan, logo etc. make up a “brand”).
Knowledge of the value contribution of these assets – the building blocks of enterprise value - and the linkages between them is essential for appropriate management and investment, which inevitably leads to competitive advantage and further opportunities to build value. The interplay between different assets depends upon: the quality of the IP and its management; the industry; the country; and the stage of life of the business among other factors.
An illustration of how IP interacts in stages of the life of a business can be seen below. Innovation is important to start with, but this drives reputation, which adds value and can sustain a company through periods of lower innovation. Knowledge of these interactions helps to understand what rates should be charged but also how to focus investment.
As marcas trabalham com outros intangíveis para criar valor e crescimento ...
É importante realizar a devida diligência sobre quais ativos intangíveis você tem, o que eles fazem e como eles interagem com outros ativos, os riscos e as atividades em sua demanda e prospectiva. Os mapas de valor podem ser usados para identificar esses links com outros recursos e a importância relativa de cada ativo dentro de um negócio. As marcas, em particular, possuem uma mistura de ativos geradores de valor mútuos e atividades relacionadas geralmente possuíam e gerenciadas em muitas partes diferentes de um negócio.
Understanding the way your assets link together to drive demand and efficiency – and therefore the value of your business – should be a top priority. Value maps can be used to identify these links with other resources and the relative importance of each asset within a business.
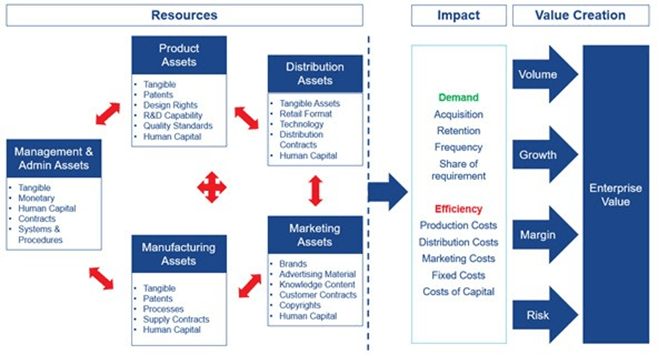
It is important to note that these value maps are most relevant when brought down further to the different asset classes. Brands, in particular, have a mixture of mutual value-generating assets and related activities often owned and managed in many different parts of a business.
Compreendendo o ciclo de feedback do posicionamento, até e de volta das alavancas, atitudes e comportamentos de marketing pode ajudar a identificar o que precisa ser ajustado para melhorar a demanda e, portanto, a lucratividade. Também pode ajudar a identificar um desempenho ruim internamente, ou dentro de um mercado, na primeira oportunidade. Uma visão geral deste mapa de valor para marcas e marketing pode ser visto abaixo. Isso muda sua probabilidade de comprar, agitar ou comprar mais serviços. Ter uma visão sobre essas conexões pode destacar o que precisa ser aprimorado para capturar mais valor da marca-licenciado ou não. Ao determinar o valor das marcas e outros ativos intangíveis para um novo negócio, você avalia o valor deles revisando a elevação incremental em valor do uso. Ao determinar o valor deles em um negócio existente, você precisa desagregar o valor deles do valor total da empresa - por exemplo, o que aconteceria se você perdesse a marca? Essas empresas tendem a exibir características semelhantes:
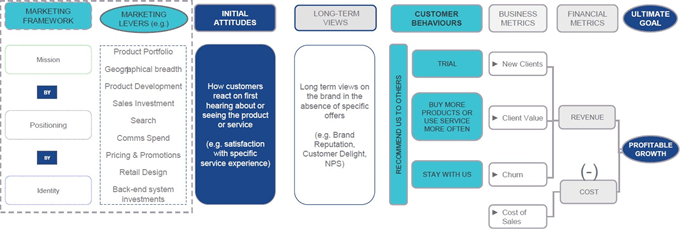
Changes in marketing frameworks and levers impact on how customers interact with and feel about the business and its brands. This changes their likelihood to purchase, churn or buy more services. Having a view on these connections can highlight what needs to be improved to capture more value from the brand – whether licensed or not.
The direction and extent of the inter-resource and activity resource relationships, as well as their relative importance as value drivers, can be estimated using a combination of: market research, statistical analysis of historical data, and Delphi techniques. When determining the value of brands and other intangible assets to a new business, you assess their value by reviewing the incremental uplift in value from use. When determining their value on an existing business, you need to disaggregate their value from the total enterprise value – for example, what would happen if you were to lose the brand?
How do you ensure your internal or external brand licensing ecosystem maximises the benefits and minimises the risk?
Many companies have used structured internal or external brand licensing programmes to build incredible businesses. These companies tend to exhibit similar traits:
Uma divisão dedicada ou uma Brandco:
divisões de gerenciamento de marca dedicadas ou "brandcos" (empresas internas e de grupo criadas especificamente para possuir e gerenciar as marcas) são mais ou essenciais para a gestão coerente, de um portfólio que não são mais essenciais. Relacionamentos de licenciados, garantam a conformidade com o arquivamento da marca registrada e a adequação da amplitude de suas marcas comerciais, gerenciamento de marcas como o fornecimento de diretrizes ou conteúdo de comunicações, avaliação de desempenho e muitas outras funções intimamente relacionadas que precisam ser consideradas em tandem. Isso geralmente está no formato de uma taxa de royalties, mas em alguns casos é um acordo simples de compartilhamento de custos. A estratégia da marca é organizada e gerenciada centralmente. Todas as partes que usam e fornecem os ativos são contratualmente obrigadas a usá-las de maneiras pré-sancionadas. Isso geralmente leva à separação de decisões amplas e estratégicas de investimento de atividades táticas de curto prazo, que ajudam a criar marcas e IPs como ativos estratégicos, e não apenas como recursos táticos. A especialização e centralização das funções também geralmente levam a sinergias de custo.
This usually involves having dedicated teams to provide overall strategy, support licensee relationships, ensure trademark filing compliance and the adequacy of the breadth of your trademarks, brand management like provision of guidelines or communications content, performance evaluation and many other closely related functions that need to be considered in tandem.
This function then extracts part of the value exploited by the companies operating the brand to recompense itself for the value it creates and shares through its services and assets. This is usually in the format of a royalty rate but in some cases is a simple cost-sharing arrangement.
This provides a number of important benefits:
Better brand and IP management. Brand strategy is centrally organised and managed. All parties using and providing the assets are contractually bound to use them in pre-sanctioned ways. This generally leads to the separation of broad, strategic investment decisions from short- term tactical activities which helps to build brands and IPs as strategic assets rather than solely as tactical resources. The specialisation and centralisation of roles also usually leads to cost synergies.
Governança e controle mais apertados. É mais fácil criar uma abordagem internacional consistente para garantir que as marcas/patentes sejam registradas e renovadas e que todas as ações necessárias para proteção sejam perseguidas com o vigor apropriado. Isso é particularmente importante, uma vez que a ação legal é frequentemente transfronteiriça. Licenças internas e externas com a entidade única esclarece os direitos e responsabilidades e, em seguida, uma equipe central tem a tarefa de garantir a conformidade de uma maneira justa e consistente em todos os usuários.
Alocação de recursos mais eficiente. As marcas podem demonstrar sua contribuição financeira para os negócios por meio de uma demonstração de resultados separados, justificando melhor os investimentos de marketing e demonstrando o ROI. A criação da receita de royalties também cria um saldo de caixa que pode ser usado para reinvestir na construção da marca. Preços
It also avoids internal companies or divisions from taking valuable intellectual property for granted and damaging them through misuse and builds a focus in functions like finance and legal about the benefits and value of strong intellectual property.
Higher earnings from external licences and clarity on internal prices. Uma BRANDCO opera como um centro de lucro, permitindo que as estruturas de incentivo para a gerência maximizem as receitas de licenciamento de marcas de terceiros. Além disso, de Brandcos, as marcas podem ser licenciadas com mais eficiência em áreas não-core de negócios, criando novos fluxos de receita. padrões e experiência. Isso começa com a cuidadosa seleção de mercado e seleção de franqueados. No entanto, também envolve um mapeamento claro de como o valor está sendo criado pela marca e IP e auditorias regulares de qualidade de todas as áreas da marca e dos negócios para garantir a qualidade perfeita. Obviamente, isso também significa que os licenciadores precisam estar preparados para cancelar as licenças para sub-desempenho ou não conformidade. Os negócios fáceis (da fama da EasyJet), por exemplo, tentaram licenciar sua marca nos anos 2000, mas foram forçados a reduzir sua expansão como resultado de dificuldades para manter a qualidade e a consistência do serviço em todas as plataformas - o que levou a deteriorar as percepções de qualidade em seus negócios. Refere -se àqueles que são tão amplamente licenciados, com tão pouca consideração pela qualidade de oferecer que a reputação da marca em todas as categorias diminua. Obviamente, isso, por sua vez, leva a menor demanda e prêmio de preço e a perda resultante na capacidade de extrair royalties. Isso inclui uma experiência clara e convincente do cliente, uma identidade consistente da marca, comunicações e mensagens (com o mínimo de alfaiataria local necessário), sistemas de treinamento e compras para citar alguns dos mais importantes. Compartilhar custos de marketing e desenvolvimento e alguns retornos podem ajudar a criar participações nos negócios gerais-levando a inovações e apoio que beneficiam todos os licenciados. Ele desenvolveu o que agora é considerado um programa de treinamento lendário, que envolve o seguinte:
Finally, external licenses can help prove the appropriate price for internal license rates to tax authorities – often difficult to do with only third-party comparisons.
Strong Oversight and Planning:
The brand and brand experience are closely controlled in order to maintain the highest operational standards and experience. This begins with the careful market selection and franchisee selection. However, it also involves a clear mapping of how value is being created by brand and IP and regular quality audits of all areas of the brand and business to ensure seamless quality. This also obviously means that licensors need to be prepared to cancel licenses for under-performance or non-compliance.
Where this goes well you shouldn’t notice it, however, where it doesn’t you do. The Easy business (of EasyJet fame), for example, attempted to license its brand in the 2000s but was forced to scale back its expansion as a result of difficulties maintaining quality and consistency of service across all platforms – which led to deteriorating perceptions of quality in its core businesses.
Similarly, the Pierre Cardin brand has even created its own verb in the vocabulary of licensing – the “Cardinisation” of brands refers to those that are so widely licensed with so little regard for the quality of offering that the brand’s reputation in all categories decreases. This, of course, in turn leads to lower demand and price premium and the resultant loss in ability to extract royalties.
Integrated and Diverse Processes & Systems:
They have impressive control processes and management systems for all aspects of managing the franchise. These include a clear and compelling customer experience, a consistent brand identity, communications and messaging (with minimal necessary local tailoring), training, and procurement systems to name a few of the more important.
One thing that should be kept in mind is that this system of support does not necessarily need to be directed from the centre. Sharing marketing and development costs and some returns can help to build stakes in the overall business – leading to innovations and support which benefits all licensees.
Case Study: Ritz-Carlton
Ritz-Carlton is recognised as delivering one of the highest levels of customer service and satisfaction – across all of its 87 hotels and in 29 countries. It has developed what is now considered a legendary training programme, which involves the following:
- Todos os funcionários devem participar do Programa de Treinamento de Atendimento ao Cliente de 'Padrões de Ouro' (os funcionários também carregam um cartão de treinamento de tamanho de carteira o tempo todo). Padrões. Aprenda os princípios de serviço Ritz-Carlton. Com mais de 35.000 restaurantes em todo o mundo (80% dos quais são franquias), é fundamental que o McDonald's permaneça em contato com a mudança de gostos dos consumidores. Especialmente no setor de restaurantes/alimentos, esses gostos em evolução são extremamente diversos e podem mudar rapidamente, dependendo da região, religião e época do ano.
- Ongoing training of 100 hours per employee and test to certify “loyal service” after one year.
- Leadership training about any changes to the brand and Brand Standards.
- Periodic ‘refresher’ courses, with ‘Brand immersion’ sessions provided every 2 years.
- Annual Managers Conference for all Franchisees.
Under the Ritz-Carlton Learning Institute and Ritz-Carlton Leadership Center, the hotel now also operates major service training operations where executives from other major brands worldwide and across many disciplines come to learn The Ritz-Carlton principles of service.
Case Study: McDonald’s

McDonald’s has one of the most synergistic working relationships with its franchisees across the entire franchise industry. With over 35,000 restaurants across the globe (80% of which are franchises), it is fundamental that McDonald’s stays in touch with changing consumer tastes. Especially in the restaurant/food sector, these evolving tastes are extremely diverse and may change rapidly depending on the region, religion and time of year.
Para conseguir isso, a empresa procura obter maior profundidade e amplitude das idéias do consumidor para informar e inspirar sua tomada de decisão empregando ferramentas como:
- Fins de semana de criação, gastos com grupos de consumidores, funcionários e franqueados para ajudar a desbloquear insights sobre como criar um melhor negócio. Estudo. No entanto, muitos dos melhores e mais bem-sucedidos licenciadores identificam a cobrança apropriada para uma marca e outro IP com base na análise dos primeiros princípios do valor que eles geram para um negócio em questão. Atividades:
- Ethnographic research complemented by a 4,000-sample usage and attitude study.
- Continued use of the brand’s established quantitative tracking tools
- The Breakfast Menu, the Fish Sandwich and most of the successful menu items have all come from franchise owner’s suggestions.
Attention to Detail on Licence Pricing and Royalty Rates:
Many businesses determine royalties based on historic royalty agreements or profitability in similar sectors. However, many of the best and most successful licensors identify the appropriate charge for a brand and other IP on the basis of first principles analysis of the value that they generate to a subject business.
To do this, the performance of the brand should be measured and monitored not only in terms of traditional core brand metrics but in financial, bottom-line value-based terms – what is the incremental ‘brand contribution’ to brand value and to business value from brand activities:
- Para o negócio de licenciado?
- para o proprietário da marca? Scorecards de marca específica do mercado e para atualizar os modelos de avaliação em intervalos regulares. A adoção de uma nova marca. A abordagem baseada em valor permitiu que casos de negócios credíveis fossem construídos para justificar cobranças para os acionistas do mercado. Maximize o desempenho coletivo para obter um grupo 'Ambição da marca'.
‘Baseline’ brand and business valuation models built, for each licensee market and for the brand owner.
Target KPIs set to promote the desired management behaviour so brand marketing activities contribute to value creation.
Brand Health Tracking and Customer Satisfaction tracker data used to populate market-specific Brand Scorecards and to update the valuation models at regular intervals.
Periodic Review meetings with licensees to check progress against targets, modify strategy and activities as appropriate and share learnings.
Case Study: Multinational Telco Operator
In collaboration with Brand Finance, a multinational telco based across MENAA used brand contribution ‘uplift’ to establish the value created from the adoption of a new brand.
- The uplift in brand and business value, with calculations for economies of scale and central brand group savings in marketing, was used for each market as a basis for apportioning value gained and calculating an appropriate payment fee back to the brand owner. The value-based approach allowed credible business cases to be constructed to justify charges to in-market shareholders.
- Ongoing, market KPIs include both traditional brand metrics and financial value-based metrics.
- Targets by market positioned as a mechanism to help align suitable resources and management behaviours behind a shared goal, rather than an overt ‘means to control’.
- For the brand owner, this should maximise collective performance to achieve a Group ‘brand ambition’.
- 6 revisões mensais planejadas para todos os mercados. Externamente geralmente envolve premeditação e estruturação inteligente do modelo. As etapas gerais para garantir que isso seja feito corretamente são as seguintes:
- The process captures learnings from around the system which can be shared across the Group and discussed in management forums.
Conclusion
Creating a system of central ownership and management for the purposes of managing and licensing brands and IP either internally or externally usually involves forethought and intelligent structuring of the model. The general steps for ensuring that this is done right are as follows:
- estabelecer o papel do licenciamento da marca: mapa de auditoria e valor toda a propriedade intelectual disponível; criar e atualizar materiais para justificar o valor da marca e do IP para todos os usuários; criar uma divisão de negócios separada para a propriedade e licenciamento de marca e IP; Verifique se há tempo e dinheiro de gerenciamento suficientes para apoiar a equipe e quaisquer alterações. determinar o ritmo e a direção do crescimento; Realize uma avaliação de risco para garantir que o IP não seja danificado desnecessariamente. criar obrigações contratuais a serem apoiadas por incentivos e orientações; Crie diretrizes claras e critérios de sucesso para apoiar e julgar licenciados.
- Develop the strategy for brand licensing growth: Consider expansion options for core and non-core segments separately; determine the pace and direction of growth; conduct a risk assessment to ensure the IP is not damaged unnecessarily.
- Build out the model for investment and governance: Create an integrated brand licensing proposition including but not necessarily limited to brand and core intellectual property; create contractual obligations to be supported by incentives and guidance; create clear guidelines and success criteria to support and judge licensees.
- Determine the structure for brand licensing payments and royalty fees: Identificar continuamente os royalties apropriados usando a análise dos primeiros princípios dos métodos de avaliação suportados por outras análises; Mantenha a estrutura de taxas simples; Seja confiante, mas não explorador com a taxa que você planeja cobrar. No entanto, para fazer isso, requer algumas premeditação e-em muitos casos-uma limpeza das estruturas existentes. Os casos de Apple, Amazon, PWC, Orange, Shell, Coca-Cola e o Ritz entre a longa lista de promulgar esse tipo de modelo mostra que trazer marcas e IP para o centro da sua empresa traz dividendos fortes. Estratégia
Business structures that involve a form of brand licensing help to put brands and IP in a firm and important position in a business – linking them directly to returns creates an incentive to maximise their benefit. However, to do so, requires some forethought and – in many cases – a clear-up of existing structures. The cases of Apple, Amazon, PWC, Orange, Shell, Coca-Cola and the Ritz among the long list of enacting this type of model shows that bringing brands and IP to the centre of your business brings strong dividends.
If you want to ensure the continued success of your brands and other IP – make sure it is properly accounted for, managed and invested in.